The basis of the calculation of the genetic proximity between two languages is a comparison of the consonants contained in a word in a language and in the corresponding word in the language it is being compared to (cognate scoring). The order in which these consonants appear in the words is being taken into account.
Consonants evolve much more slowly than vowels. In comparison with human bodies found on archaeological sites, vowels can be compared with the skin and consonants with the bones. Only bones remain over longer periods in a recognizable shape. In comparative linguistics, consonants are the "words' bones"!
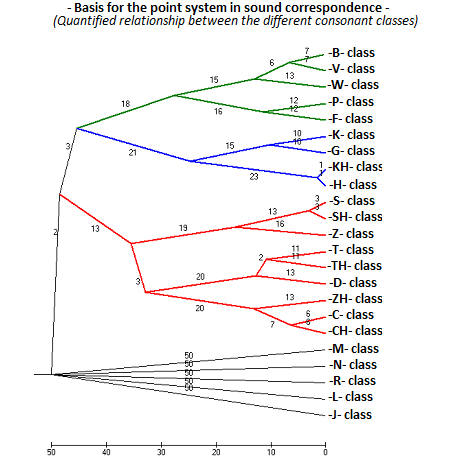
In this project, the consonants are organized in classes: the hundreds of consonants used in world languages are gathered in related classes ('-K-' class, '-B-' class, etc.). The extreme simplification in the sound change modelization for the computer processing appears to deliver sharper results than more complicated models. Moreover, as we here compare languages across world wide spread families, we have to take only universal sound change into account.
Here are the classes into which the consonants are regrouped for this project. Their frequency in the complete word sample and the number of points they generate if occurrences are identified in the word comparisons are listed bellow. Exact matches get the highest score, but matches across related classes also get points – decreasing according to how remotely related this
relationship is. The quantification of the consonant relationship for the point system is established partially with data from: "Sound Correspondences in the World's Languages (Cecil H. Brown, Eric W. Holman and Søren Wichmann)".
The values from Cecil H. Brown, Eric W. Holman and Søren Wichmann's study were initialy partially used, converted and adapted to the elinguistics.net consonant grouping model. This reference contains much more relationships between consonants and do so in a much finer granularity. In elinguistics.net, not all relationships between consonants are needed, but only those giving stronger signals in cognate identification
with a low exposure to chance. During our research "Stochastic approach to worldwide language classification: the signals and the noise towards long-range exploration" we implemented a machine learning approach to refine the point system which we finally decided to use in eLinguistics.net
as well. Generally speaking, some complex relationships between consonants as known in sound change in various languages are not modelized when they bring a bigger exposure to chance matches. Finding out when this is the case was the challenge of the machine learning approach.
|
Consonant class -B- (b) b, б, ب, Hindi "ब, भ", Urdu "ب بھ",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-B-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -C- (ts, dz, tʃ) ts, German "z" (partial), Slavic "c", Cyrillic "ц",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-C-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -CH- (tʃʲ) tch, German "tsch", Slavic "Č", "ч", Armenian "չ", Kurdish "Ç", Polish "cz", Croatian/Serbian, Polish "ć", Armenian "չ", " ջ", Cyrillic "ч", Hindi "छ", Persian "ﭺ",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-CH-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -D- (d, dˁ) d, д, Arabic "د, ض", Hindi "द",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-D-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -F- (f, ɸ) f, ф, ف, Afrikaans "v", Dutch "v", German "v",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-F-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -G- (g, ɟ) g, г, Persian, Pashto "ﮔ", Hindi "ग, घ",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-G-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -H- (ħ)
h, Arabic "ح, ه",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-H-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -J- (j) French "ll", Hindi "य", Arabic "ي", Slavic "j", Various languages "y" as consonant,... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-J-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -K- (k, q) k, q, Italian "ch", "qu", "cq", French "qu", Catalan "q", Galician "c", French "c" (partial), Celtic "c", Arabic "ك, ق",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-K-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -KH- (x, χ, ɣ ç) Cyrillic "х", Afrikaans "g" (except between "l/r" and "e"), Dutch "g", German "ch", Spanish "j", Croatian/Serbian "h", Greek "χ", Gothic "X", Breton "c'h", Irish, Welsh "ch", Arabic "خ",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-KH-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -L- (l, ɬ ʎ) l, л, ل , ल, Welsh "ll", Polish "ł",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-L-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -M- (m, m̥) m, م, म,... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-M-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -N- (n, ɳ, ɳ̊, ɲ̊, ɲ, ŋ̊, ŋ, ɴ ) n, Polish "ń", ن, न,... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-N-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -P- (p) p, п,... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-P-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -R- (r, ʁ ʀ ɾ, ɽ) r, Cyrillic "р", Arabic "غ and ر", Hindi "र" Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-R-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -S- (s, sˁ) s, Cyrillic "с", Arabic "س, ص",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-S-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -SH- (ʂ ʃ) Afrikaans "sj", German "sch", "s" before "t", French "ch", Slavic "Š", Polish "ś", Arabic "ش", Cyrillic "ш",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-SH-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -T- (t, tˁ) t, Arabic "س, ص",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-T-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -TH- (θ, ð) th, Gothic "þ", English "th", Cornish "dh, th", Celtic "th", Arabic "ث ذ", Hindi "थ, ध, ठ, ढ",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-TH-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -V- (v, ⱱ) v, Cyrillic "в", Afrikaans "w" except after "d, k, s, t", Dutch "w", German "w",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-V-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -W- (w) English w, Afrikaans "w" after "d, k, s, t", Gothic "ƕ",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-W-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -Z- (z) z, Cyrillic "з", German "s" (partial), French "s" (between two vowels), Arabic "ز, ظ",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-Z-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -ZH- (ʒ, ʑ, ʐ dʒ) Slavic "ž", French "j", Catalan "j", Hindi, Sanskrit "ज", Arabic, Pasto, Persian "ژ", Irish, Scottish Gaelic "dh", Polish "ź, ż", Cyrillic "ж",... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-ZH-' correspondences |
|
Consonant class -7- (ʔ) Arabic Hamza "ء", Hebrew Aleph "א", Polynesian languages "ʻ" like ʻokina in Hawaiian and Samoan,... Details about the correspondence point system click here: Class '-7-' correspondences |
Here is the consonant class point system used between 2015 and May 2023
Values generated from the old system are still available at: Compare languages - version 2017